Understanding and Finding the Right Home Charging Solution for EVs
This guide will provide the basics to home charging solutions, where to find incentives, electrical terms and demystifying electric fueling.
Grant Gerke, EV Ambassador, @PluggedInEv

While there can be complexities and nuances with home charging solutions, the concept is simple: electric fueling. The guide will educate newbies on amperage, volts and kWs, and provide EV owner insights on charging station incentives and installation.
Things To Know about Home Charging Stations:
Electrical Engineering degree? Not needed. The electrical terms provided below will help newbies communicate with an electrician when discussing a home charging station. Once installed, daily charging is easy: open the charge port and plug in to the car.
What’s the difference between a charger and Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE)? The “charger”, top image, connected to wall is actually Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment or a provide of electricity, simply. Technically, the “charger” is onboard the EV for all major brands — turning AC into DC. But, for our purposes, we will call a EVSE a charging station.
Why should I purchase a level 2 charging station? A level 2 charging station electrical requirements are equivalent to a washer/dryer unit. It’s an easy job for a qualified electrician. And the amount of EV range that is received from a Level 2 charging makes driving electric rather easy. Depending on the EV’s acceptance rate — see Plugged In’s EV glossary — and amperage in the electrical cabinet, a battery pack can receive anywhere from 12 to 55 miles of charge per hour.
What’s going on during Level 2 charging? The charging station is taking AC electricity from the circuit and converting it to DC electricity for the battery pack inside the EVs. All major EVs have an onboard chargers that converts AC to DC inside the car.
Safety: Home chargers are very safe and have many safety ratings tied to them, such a NEMA 3 and NEMA 4x ratings that guarantee use for outdoor use — NEMA 4 is higher strength rating. Similar to Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI) found in homes, these chargers protect from electricity surges and stop charging after any leakage of electricity. The cables for charging stations have an IP65 rating, which have water ratings that usually pertain to industrial manufacturing environments — keeps rain or snow out while being used outdoors.
Charging Station Installation
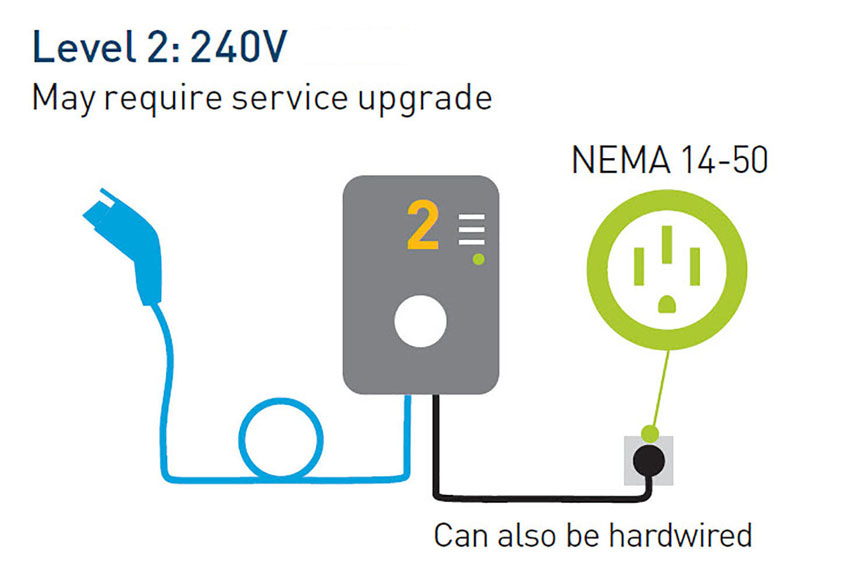
To support a Level 2 EV charging station or insert a new 14-50 or 6-50 outlet in a garage, a home charging station needs a 240V or 208V AC plug and 40 to 80 Amp circuit. I would recommend a certified electrician to do the installation, which includes adding capacity to the electrical box and setting up conduit from the circuit board to the location of the charging station. Adding conduit can be costly with a detached garage and the circuit breaker is located in the house — up to $2,000 sometimes.
If you take away one thing from this guide, get an estimate for the work to be done. I always like to avoid surprises. Both of my installations were under $600, one was about $175 with the minimal conduit, which carries wires, needed.
Via a Reddit message board:
truthseeker, in our area (Colorado - Denver Metro area) it is usually about $300 to $500 in installation labor (electrician) plus the cost of the charger (~$500).
Amperage, Voltage and kW
Voltage and amperage are two measures of electrical current or flow of electrons. Voltage is a measure of the pressure that allows electrons to flow, while amperage is a measure of the volume of electrons. For a Level 2 Charging station, a 240V electrical current is required and a qualified electrician will be more than qualified for this work. kW measures electrical power and this is used for the vehicle’s acceptance rate — or known as car charging rate (see image below). The higher the kW means a quicker charge from a Level 2 station.
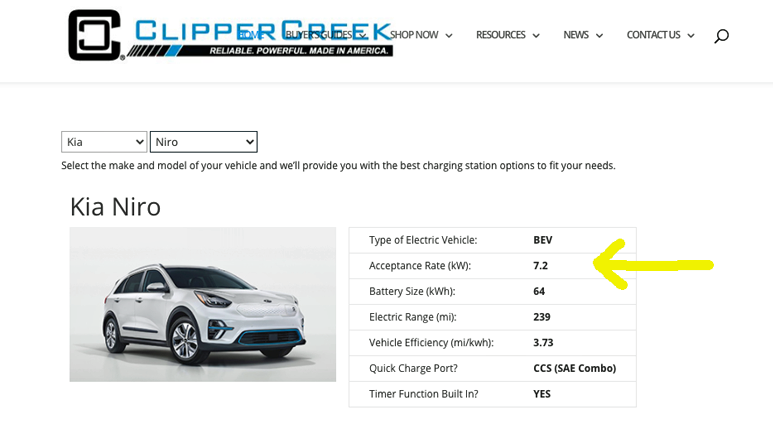
For example, a Kia Niro has a 7.2 kW acceptance rate that provides about 30 miles in an hour from Level 2. And the same number of miles, approximately 30 miles with 32 amps circuit, applies for Tesla vehicles using its Universal Mobile Connector from a 14-50 outlet.
Location, Location, Location
Where’s the ideal location for a Level 2 charging station in a garage? Things to consider are the length of cable and the EV charge port location. Like some gas cars, the port can be on the driver or the passenger side of the car towards the trunk. For example, the new Volkswagen ID.4 has the charge port located on the passenger side in the rear, and all Teslas in the U.S. have it on the driver-side rear. However, the Hyundai Kona and Nissan Leaf have the port located in the front, by the bumper (see above).
For chord length, it varies and longer is better. The length can vary from 16 to 28 ft. Most early adopters and EV buyers narrow down their search to one or two EVs toward the end, so understand where the charge port is located and proceed accordingly.


Incentives
As mentioned in an earlier Plugged In article, utilities are rolling out EV incentive programs — who doesn’t love a rebate! — to customers for installation and also time-of-use (ToU) programs, where energy is sold wholesale. ToU programs take advantage of excess energy on the grid at night and sell it at lower rates, which is ideal for Level 2 charging solutions. As mentioned, level 2 will “top-off” a car in about two hours for daily use. Also, in California, there are tier programs depending on the time of day. A Level 2 smart charger — connected to a wireless network — is more expensive but provides convenience in allowing an owner to start a charge from a smartphone app.
Brands
When it comes to charging stations, there are many out there and Enel X, Clipper Creek, Siemens and Tesla have their own stations. In our next newsletter, Plugged In will provide a great resource on evaluating home charging stations.
And later this summer, Plugged In will have a follow-up on how to future-proof an EV household for charging.
Please share this newsletter with anyone that may be interested in buying an EV!

